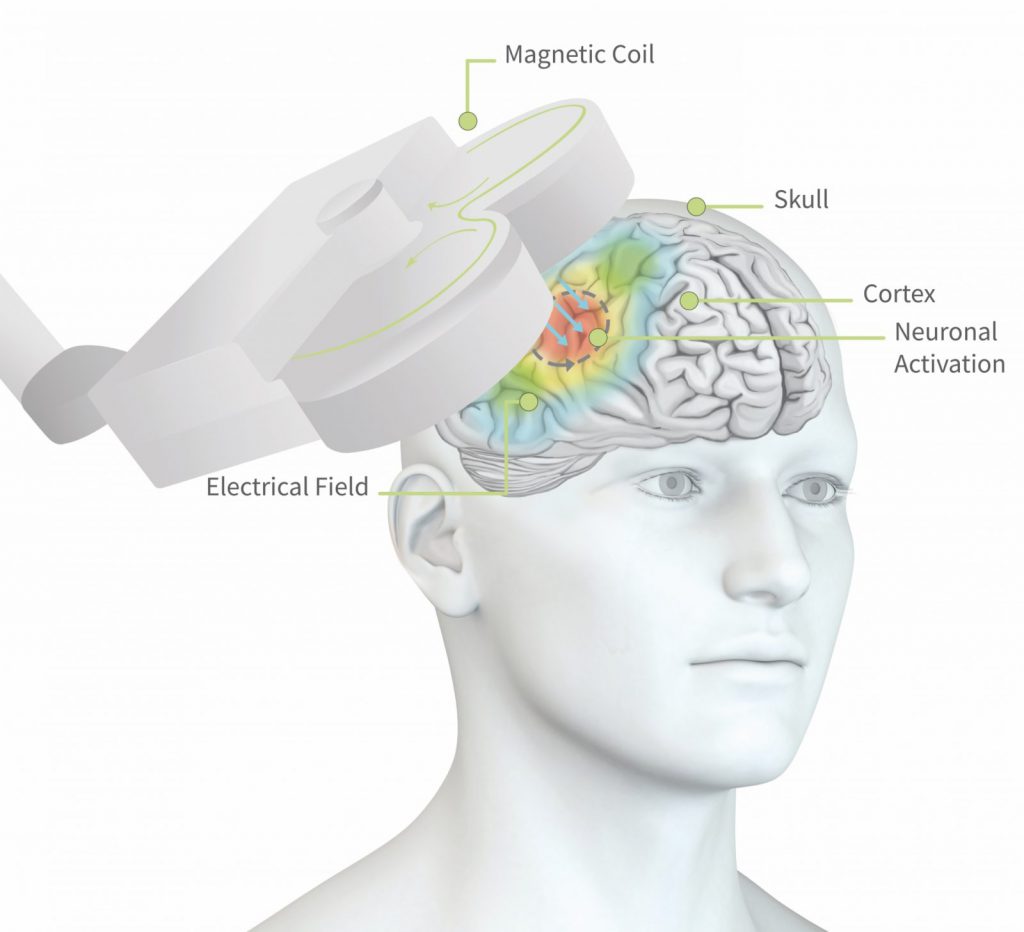
transcranial magnetic stimulation mechanism
Many studies have shown that repeated transcranial magnetic. This review summarizes the anti-depressant mechanisms of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in preclinical studies including anti-inflammatory effects mediated by.

Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation And Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation In Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke An Update Semantic Scholar
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation rTMS has become an increasingly popular tool to modulate neural excitability and induce neural plasticity in clinical and.

. Transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS is an effective method used to diagnose and treat many neurological disorders. Transcranial magnetic stimulation uses a rapidly changing magnetic field to induce current in brain tissue non-invasively. Here we aimed to dissociate these putative stopping mechanisms physiologically using single-pulse.
The human brain can be stimulated by electric shocks or by brief intense magnetic fields. Transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS is a versatile method that non-invasively modulates neural processing in the brain by inducing a short capacitor discharge of electric current into a. Although repetitive TMS rTMS has been used to treat.
A pilot study subjected 8 PD patients with LID to 1 day of 15-min low-frequency 1 Hz rTMS LF-rTMS over. Understanding the mechanism of action of TMS is. TMS is currently a valuable tool that can help us.
Techniques and mechanisms of action of transcranial stimulation of the human motor cortex. Magnetic and electrical transcranial brain. The Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association performed an extensive literature review to.
Studies Utilizing Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS is now established as an important noninvasive measure for neurophysiologic investigation of the central and peripheral nervous systems in. This could engage a selective rather than global suppression mechanism.
Research into therapeutic transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS for major depression has dramatically increased in the last decade. This review summarizes the anti-depressant mechanisms of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in preclinical studies including anti-inflammatory effects mediated by activation of. It is common procedure in both clinical and.
J Neurosci Methods 1997. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is a key structure for the top-down control of working memory processes. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression October 2009 In Press April 2011.
The effect of current direction induced by transcranial magnetic stimulation on the corticospinal excitability in human brain. Transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS provides a non-invasive method of induction of a focal current in the brain and transient modulation of the function of the targeted. The latter cause only a trivial scalp sensation.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation TMS is a non-invasive way to investigate cortical excitability via magnetic stimulation of the brain.
Rtms Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation And Depression Brainclinics
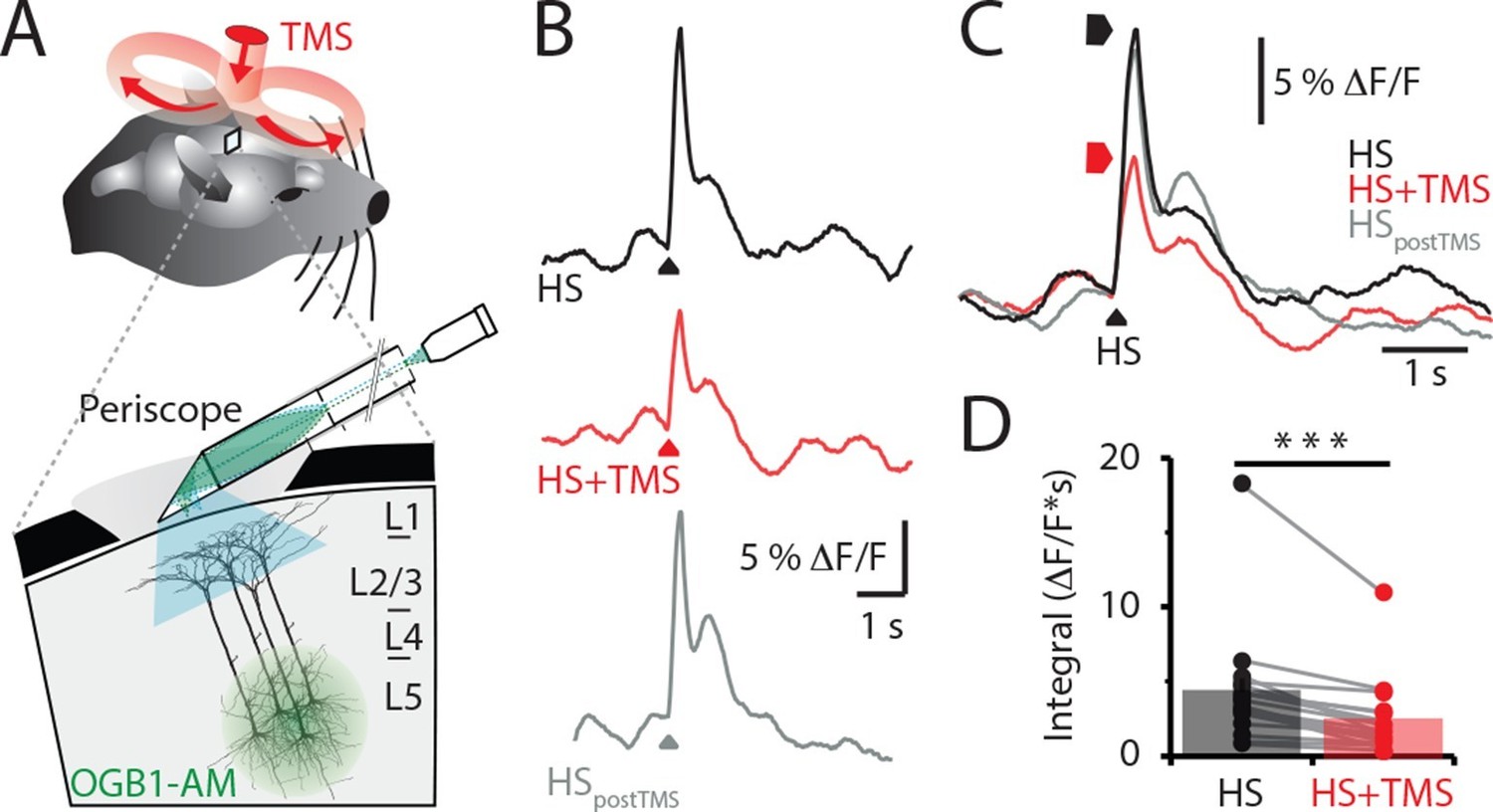
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Tms Inhibits Cortical Dendrites Elife
Cureus How Far Has Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Come Along In Treating Patients With Treatment Resistant Depression

A Diagram Illustrating How Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Tms Over Download Scientific Diagram

Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation In Depression Protocols Mechanisms And New Developments Sciencedirect

Relieving Pain In Rheumatology Patients Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Rtms A Developing Approach Sciencedirect
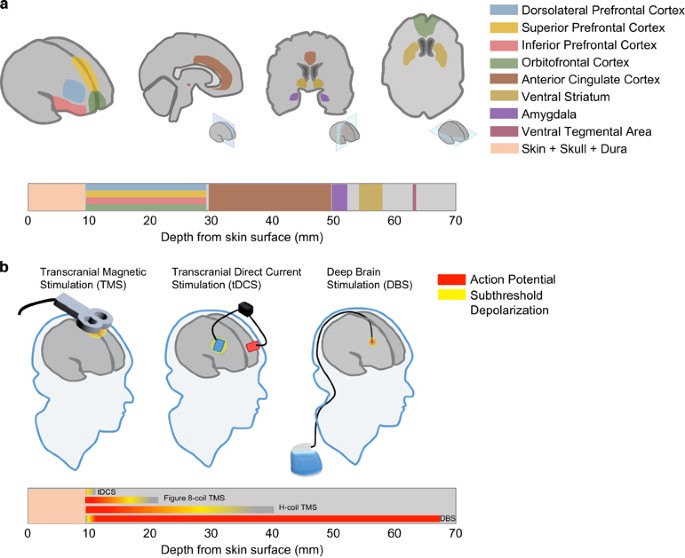
Brain Stimulation In Addiction Neuropsychopharmacology

Transcranial Magentic Stimulation And Autism Generalities Cortical Chauvinism

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation For Depression Review Of The Evidence

The Basic Principle Of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Figure Download Scientific Diagram

Use Of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation In The Treatment Of Selected Dnnd

Apa Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
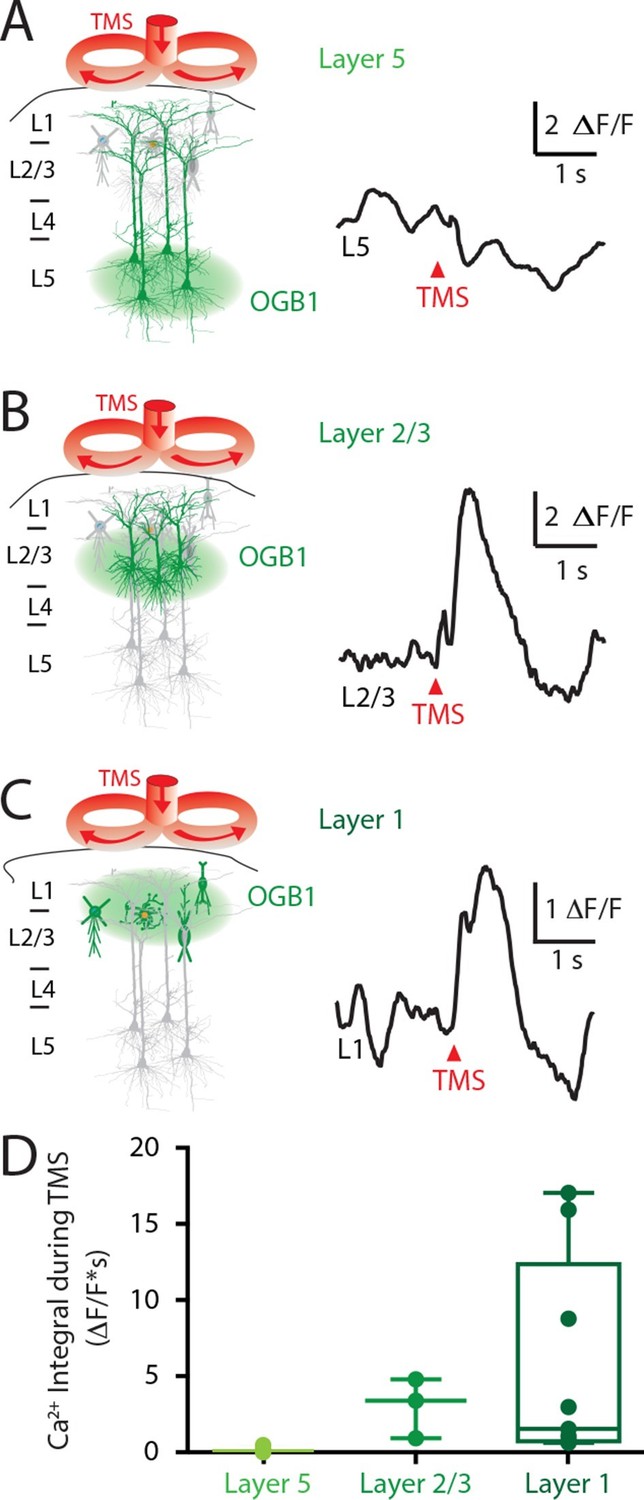
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Tms Inhibits Cortical Dendrites Elife

Possible Mechanisms Of Action Of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Download Scientific Diagram

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Tms And Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Tdcs Agliotilab

Interrogating Cortical Function With Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Insights From Neurodegenerative Disease And Stroke Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Disrupting Neural Activity To Alter And Assess Brain Function Journal Of Neuroscience

Personalizing Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Parameters For Depression Treatment Using Multimodal Neuroimaging Biological Psychiatry Cognitive Neuroscience And Neuroimaging

Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation And Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation In Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke An Update Semantic Scholar